The COVID-19 Clinical Care Pathway was updated on 10 November 2022

The COVID-19 CARE pathway is designed to be a living tool to support health care workers visualize the current clinical and therapeutic recommendations to be considered in the care plan for patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 CARE pathway is aligned with the 12th version
of the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline
published on the 10 June 2022 and the fifth version of the WHO COVID-19 Clinical management: living guidance
published on the 15 September 2022.

Confirm
SARS-CoV-2 infection
Ensure prompt diagnosis using a molecular (NAAT/PCR) or antigen-detection test (Ag-RDT).
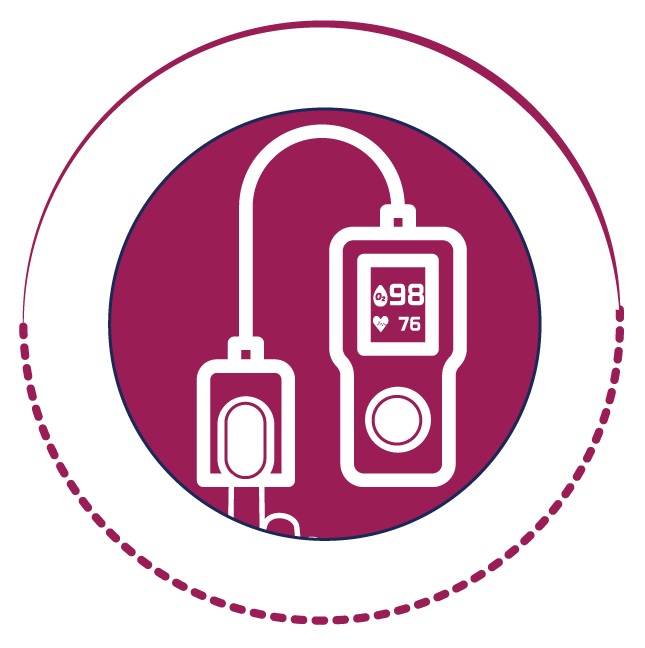
Assess
symptoms, risk factors and severity
Provide early clinical assessment and evaluation to determine if the patient has risk factors, emergency signs, or symptoms that require treatment, clinical referral or admission to hospital care.

Risk factors
- Age > 60 years
- pre-existing non-communicable disease (including hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, cerebrovascular disease, dementia, mental disorders, chronic kidney disease, obesity, cancer)
- immunodeficiency (including HIV, immunosuppressive medical treatment for rheumatoid or other autoimmune disease)
- unvaccinated against COVID-19.
In pregnant or recently pregnant women, additional risk factors are: advanced maternal age (>=35 years), obesity, chronic medical conditions, and pregnancy specific disorders (e.g. gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia/eclampsia).
Emergency signs
- obstructed or absent breathing, severe respiratory distress, central cyanosis, shock, coma and/or convulsions
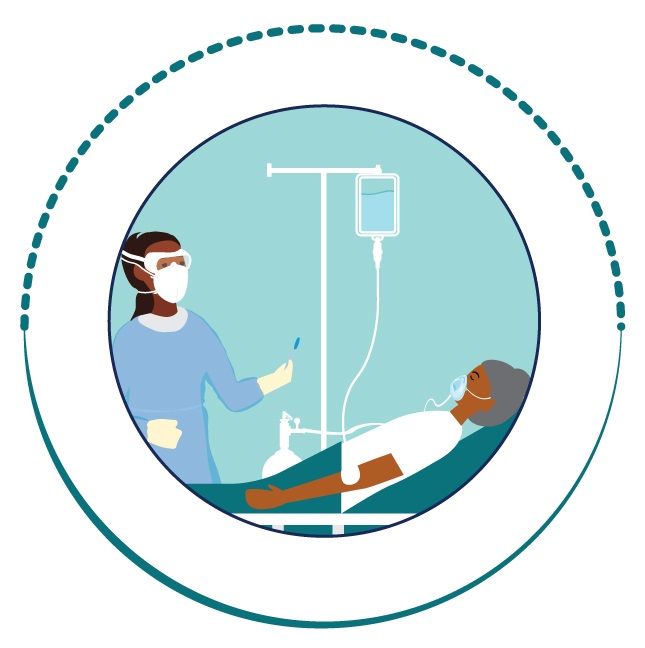
Evaluate
clinical response and recovery
All patients receiving COVID-19 treatment require clinical monitoring throughout their illness until sufficiently recovered, including those who develop post COVID-19 condition.
Immediate medical re-evaluation should occur where:
- emergency signs are present
- SpO2 <90%.
Urgent medical re-evaluation* should occur where:
- SpO2 falls to 90-94%
- Symptoms worsen
- Side-effects occur
- Other concerns arise
* if being treated at home, patients and caregivers should be counselled on important signs and symptoms (including chest pain, fast or difficult breathing, fast heart rate, palpitations, confusion). If present or worsening, instruct patient or caregivers to call for emergency help according to national protocols.
Recording and reporting
COVID-19 Clinical Care Pathway Printable Resources
The COVID-19 CARE pathway is a living tool to support health care workers visualize the current clinical and therapeutic recommendations to be considered...
Links to resources
Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline
This publication has been superseded by a new version, dated 13 January 2023.Version dated 13 January 2023The WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline...
First published in 2020, this toolkit is intended for clinicians working in acute care, managing adult and paediatric patients with acute respiratory infection,...

